Balancing People and Technology: How AI is Transforming Recruitment

Widespread skills shortages, fierce competition for top talent, and shifting candidate expectations have made recruitment more complex and less predictable. At the same time, the velocity of digital transformation has placed mounting pressure on employers to modernise their hiring strategies.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly emerging as a transformative force as a strategic co-pilot in how companies identify, engage, and evaluate candidates. From streamlining early-stage hiring processes to offering predictive insights that improve decision-making, AI is helping organisations move faster and smarter in their search for talent.
Yet, this shift is not without its challenges. Striking the right balance between automation and human judgment is now a critical strategic imperative. The future of recruitment depends on how effectively organisations can harness AI to enhance the hiring experience while preserving the human connection that lies at its core.
AI in Action: Transforming the Hiring Process
Employers are using AI to re-engineer time-consuming tasks, identify stronger-fit candidates, and create a more agile and candidate-centric hiring process.
Automated Screening & Faster Hiring
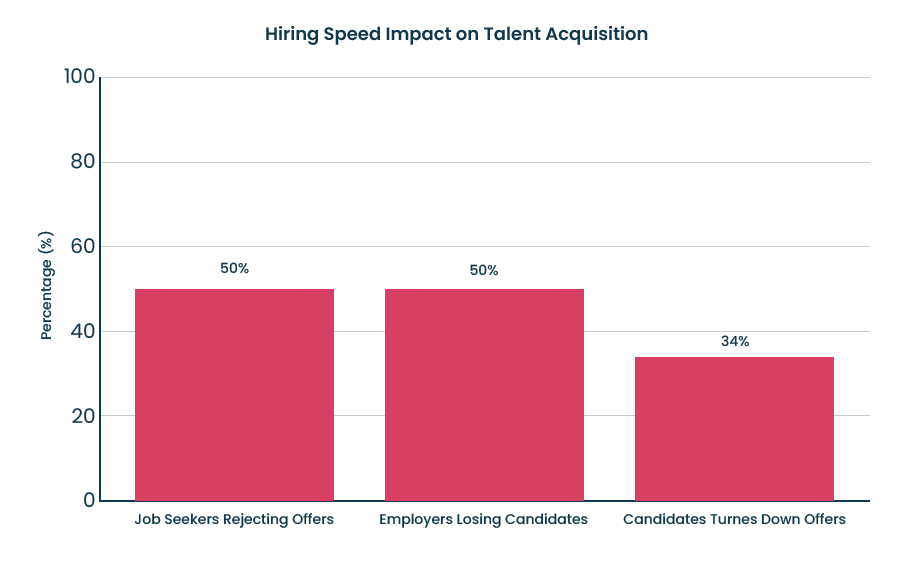
Manual CV screening is one of the most resource-intensive parts of recruitment. AI-powered tools can now analyse thousands of CVs in seconds, filtering based on job-specific keywords, required skills, and prior experience. This not only reduces the workload for recruiters but also accelerates time-to-hire. Data from the Morgan McKinley Global Workplace Trends Survey indicates that 50% of job seekers reject offers due to slow timelines, and employers lose up to 34% of candidates to faster-moving competitors.
Predictive Matching for Quality Hires
Beyond filtering, advanced AI tools are now capable of learning from previous hiring successes to identify predictive traits in new applicants. By analysing patterns across successful placements, such as skill combinations, behavioural traits, and cultural alignment, these tools provide recommendations that help hiring managers make better-informed decisions.
Enhanced Candidate Engagement
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants offer real-time communication, help applicants navigate job portals, answer FAQs, schedule interviews, and send automated updates.
Reducing Bias and Enhancing Diversity
By removing personal identifiers and evaluating candidates solely on their qualifications and experience, AI can support more equitable decision-making.
However, this potential is contingent on clean data and algorithmic oversight. Concerns remain. According to the Morgan McKinley Global Workplace Trends Survey, 71% of candidates worry about bias in AI tools, and employers must ensure their systems are transparent and regularly audited to mitigate risk.
Cost and Efficiency Gains
Automating repetitive tasks like screening and scheduling reduces dependency on manual hours. Reports from European firms show up to 36% savings in HR costs through AI implementation. In a landscape where every hire counts, this level of operational efficiency is critical.
The Human Element: Balancing AI and Intuition in Recruitment
As powerful as AI is, recruitment remains at its core, a human process. Technology can streamline tasks, speed up decision-making, and surface insights, but it cannot replicate human empathy, intuition, or cultural awareness. For organisations seeking to make meaningful, lasting hires, AI must be treated as an enhancer, not a replacement.
AI as an Assistant, Not a Decision-Maker
While AI tools can identify promising candidates and recommend matches, most hiring professionals view them as supportive tools, not final arbiters. Only 2% of hiring managers fully trust AI to make final hiring decisions. A large majority still prefer human-led judgements for assessing interpersonal skills, cultural fit, and motivation, factors that AI cannot yet quantify effectively.
This hybrid approach is gaining traction: 62% of employers acknowledge that while AI makes hiring more efficient, it has not significantly improved their overall outcomes without human oversight. The best hiring decisions typically come from a blend of data-driven analysis and real-world experience.
Soft Skills and Cultural Fit Require Human Interpretation
Technical qualifications and job experience can be quantified, but how do you assess a candidate’s ability to collaborate, lead, adapt to uncertainty, or resolve conflict? These “soft” traits are increasingly critical in today’s agile, cross-functional teams.
AI is still limited in its ability to evaluate nuanced interpersonal dynamics or judge whether someone will thrive within a specific team culture. That’s why employers continue to rely on human recruiters and hiring managers to interpret these complex, context-dependent qualities.
Candidate Perceptions: The Need for Human Touch
Candidates themselves express caution about AI in hiring. A recent survey found that 67% of job seekers feel AI-driven processes lack a personal touch, and 73% say they are less likely to pursue roles where their applications are screened solely by algorithms.
These concerns are more than emotional; they reflect a broader demand for transparent, respectful, and human-centred experiences. Especially where high-value candidates often receive multiple offers, how they’re treated during the hiring journey can be the deciding factor.
Striking the Right Balance
Companies that succeed in combining digital speed with emotional intelligence will not only improve hiring outcomes but also enhance their employer brand. They’ll show candidates that technology isn’t replacing people — it’s empowering them to connect better, faster, and more meaningfully.
Ethical, Legal and Operational Considerations
As AI becomes more deeply embedded in recruitment workflows, the ethical and legal implications are coming into sharper focus. Organisations must move beyond efficiency and innovation to ensure their AI systems are fair, transparent, and compliant, especially in regions like Europe, where data protection and algorithmic accountability are tightly regulated.
Compliance with GDPR and the EU AI Act
Recruitment processes involve sensitive personal data, and when AI is used to process that data, regulatory scrutiny intensifies. Under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), employers must ensure that candidate data is processed lawfully, transparently, and with clear consent.
The upcoming EU AI Act is expected to categorise recruitment-related AI tools as “high-risk systems.” This classification will impose stringent requirements, including:
- Risk assessments of the AI system’s impact on fairness and bias.
- Human oversight in decision-making.
- Robust documentation on how AI decisions are made.
- Transparency to candidates about how AI is used in the hiring process.
Failure to comply could result in not only fines but also reputational damage, that are expected to lead in ethical innovation.
Algorithmic Fairness and Bias Auditing
While AI can help mitigate human biases, it can also reinforce them if algorithms are trained on incomplete or skewed data. For example, if historical hiring data favours a particular gender, ethnicity, or educational background, AI may learn to replicate those biases, inadvertently excluding qualified candidates.
To address this, companies must regularly audit their AI systems for:
- Disparate impact across demographics.
- Fairness in scoring models and recommendations.
- Explainability - the ability to clearly communicate how an AI arrived at a decision.
Building a Framework for Responsible AI
Leading employers are beginning to implement internal Responsible AI frameworks, often involving:
- Cross-functional ethics committees (HR, legal, tech, DE&I).
- Clear accountability structures for AI decision-making.
- Policies on candidate notification, allowing applicants to opt out of AI-led assessments or request human reviews.
- Training for recruiters to understand how to interpret and challenge AI-generated insights.
Strategic Imperatives for Employers
As AI continues to reshape the recruitment landscape, the most successful organisations will be those that approach it not just as a technology shift, but as a strategic transformation.
Here are four key imperatives for employers looking to future-proof their hiring strategies:
1. Adopt Skills-Based Hiring
The shift away from degree-based requirements toward skills-first recruitment is gaining momentum. AI can support this by:
- Scanning candidate portfolios and GitHub activity for evidence of technical capability.
- Matching competencies with job requirements, even if formal credentials are missing.
- Highlighting adjacent or transferable skills to expand candidate pools.
According to recent findings, 57% of companies now prioritise practical skills over traditional qualifications. By redesigning job descriptions and integrating AI into assessment, employers can tap into more diverse, high-potential talent.
2. Strengthen Employer Brand Through Transparency and Inclusion
In a digital-first job market, how you recruit is a direct reflection of your brand. AI tools can help personalise outreach and optimise communication, but what truly resonates with candidates is authenticity and transparency.
Consider these actions:
- Clearly disclose the use of AI in your hiring process.
- Provide candidates with feedback or insight into how decisions are made.
- Showcase measurable progress on diversity, equity, and inclusion goals.
Job seekers increasingly evaluate employers not just on salary or job specs, but on their ethics, purpose, and workplace culture. AI can support this messaging, but the substance must come from within.
3. Embrace Flexibility as a Recruitment Differentiator
AI may not directly create flexible work policies, but it can offer insights into workforce preferences and help personalise candidate journeys. Flexibility remains a top priority for professionals:
- 66% value hybrid work above all else
- 62% have rejected offers lacking flexible arrangements
Companies that resist hybrid models or fail to codify flexibility are likely to lose top-tier candidates. By integrating AI with workforce analytics and hiring data, employers can design roles and engagement models that align with evolving employee expectations.
Human-Centred AI is the Future of Hiring
As we look ahead to 2025 and beyond, one truth becomes increasingly clear: AI is not replacing recruiters, it's redefining their role.
The integration of AI into recruitment isn’t just about keeping pace with innovation. It’s about creating smarter, fairer, and more engaging hiring experiences in a market that demands speed, transparency, and empathy. By automating repetitive tasks and surfacing deeper insights, AI allows hiring teams to focus on what truly matters — building relationships, evaluating human potential, and making decisions with long-term impact.
But with this power comes responsibility. The most effective organisations will be those that adopt AI strategically and responsibly, embedding it within a framework of trust, compliance, and human oversight.
Ultimately, the future of work belongs to employers who combine technological agility with a deep understanding of people. Those who balance cutting-edge tools with ethical leadership and blend automation with authenticity will not only attract top talent; they’ll build the kind of organisations where talent wants to stay.














